The two most popular gastric bypasses are:
- Roux en Y Gastric Bypass
- One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass
Roux en Y Gastric Bypass
This bypass has been around for more than half a century. It has proven long term results and has been found to be very effective for weight loss and improvement in health conditions.
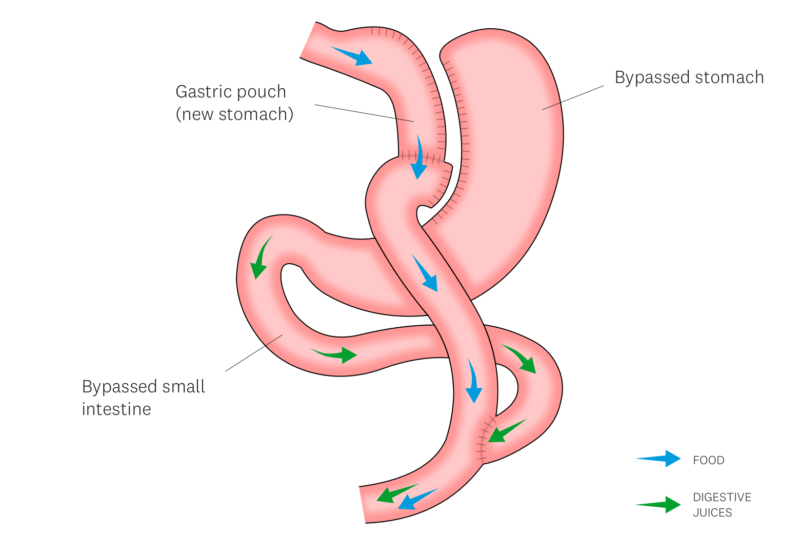
Here’s how the Roux en Y gastric bypass achieves its results:
- Reduced Stomach Size: A section of your stomach is reshaped into a smaller pouch, limiting the amount of food you can comfortably eat. This leads to earlier feelings of fullness and ultimately, lower calorie intake.
- Bypassed Intestine: A portion of your small intestine is rerouted, bypassing the original portion of your stomach and a section of the small bowel. This reduces the area available for nutrient absorption, leading to some malabsorption of calories and nutrients.
- Minimally Invasive Procedure: The surgery is typically performed laparoscopically, meaning it uses several small incisions in your upper abdomen. This translates to faster recovery times and less scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass
Also known as the Single Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (SAGB) and sometimes referred to as the Mini Gastric Bypass (MGB). It’s a variation of the Roux en Y gastric bypass.
This bypass has been around for more than quarter of a century and has proven long term results.
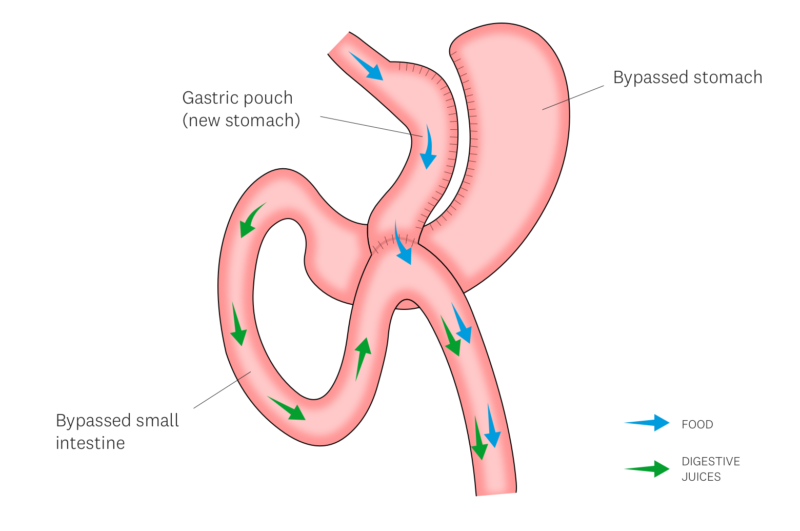
The one anastomosis gastric bypass works in a similar fashion to the Roux en Y gastric bypass:
- Curbing Portions (Restriction): A small pouch is created from your existing stomach, significantly reducing its volume. This naturally limits how much food you can comfortably eat, leading to earlier feelings of fullness and ultimately, lower calorie intake.
- Limiting Nutrient Absorption (Malabsorption): A section of your small intestine is bypassed, preventing food from reaching the first part and your original stomach. This reduces the surface area available for your body to absorb nutrients from your meals, contributing to weight loss.
- Hormonal Regulation: The surgery can influence gut hormones that control hunger and satiety. These hormonal shifts can lead to a decreased appetite and increased feelings of fullness, making it easier to manage your weight in the long term.